The transformational potential of artificial intelligence and carbon ledger technology in supply chain management cannot be overstated. As global business landscapes shift toward a stronger focus on sustainability, integrating these cutting-edge technologies into existing systems becomes increasingly important. They bring forth new avenues for increasing operational efficiency and transparency — all within the sustainability framework.
Transportation management, in particular, has emerged as a critical area where sustainability can have a profound impact. Consider the journey of a leading logistics company that effectively harnessed the capabilities of AI-driven tools to add an extra layer of sophistication and precision to existing systems. The company's transformative journey took it from traditional processes to a streamlined, AI-integrated system for improved sustainability.
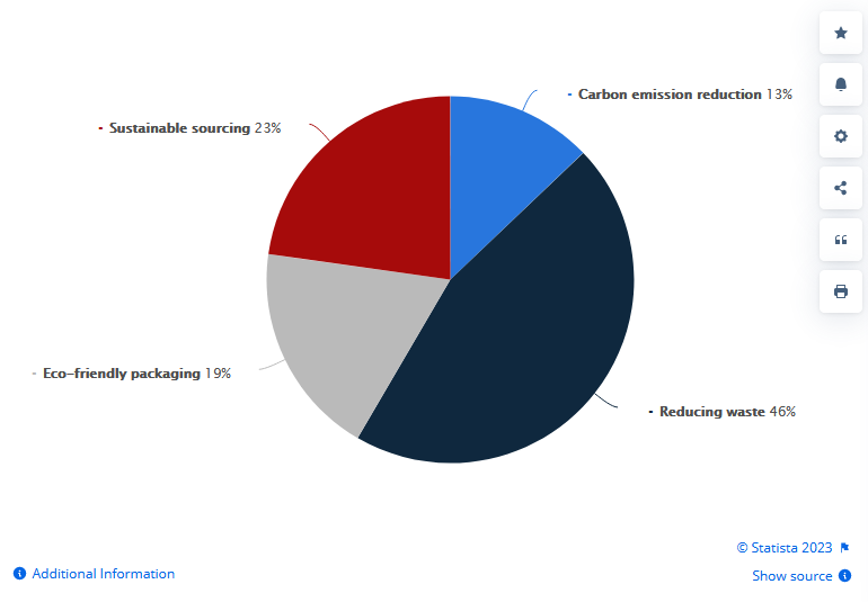
Main sustainable logistics priorities among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the U.S. as of April 2023
Source: Statista
The Challenge
Transitioning toward sustainability can be a tricky puzzle for the logistics industry. High fuel consumption, hefty carbon emissions, and the resulting environmental impact can create a dense web of challenges. The logistics company sought to align its transportation processes more closely with sustainability goals.
The answer lay in harnessing the potential of an environmental, social and governance (ESG) module embedded within the company’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Identification of ESG Data Points | Mapping/ Solution Architecture | Roadmap to ESG Reporting |
Capture and understand reporting requirements and current data sources | The initial design of future data architecture for data gathering and reporting | Execution roadmap to enable aggregation + automation for critical reporting |
Creation of an as-is ESG data model | Degree of change - from incremental to proposed changes needed in automating ESG reporting | Benchmark (where available) against the market |
Listing of source systems where data points reside | Determine opportunities and threats in markets as they change and discuss a flexible design to ebb and scale | Understand key environmental, customer, political and regulatory risks associated with sustainability |
Data Ownership per ESG data point defined/detailed |
| Aggregate data sources and list of requirements for Sprint 2 - Solution Design |
Assessment of current Sustainable Ledger / ETL / Analytical Reporting Capabilities |
|
|
The first step was a thorough identification of ESG data points. This required a keen understanding of the information needed to track and measure the company’s ESG performance. It built an “as-is” ESG data model, detailing each data point and establishing ownership.
Following the data point identification, the company delved into solution architecture. It designed a future data architecture for data gathering and reporting, bearing in mind incremental changes required in automating ESG reporting. It listed the source systems where data points reside, and evaluated their current capabilities for sustainable ledger and analytical reporting.
With the necessary data points identified and a suitable solution architecture in place, the next step was formulating a roadmap for ESG reporting. The objective was to enable aggregation and automation for critical reporting, while understanding key environmental, customer, political, and regulatory risks associated with sustainability. The company also identified opportunities and threats in changing markets, and discussed a flexible design to accommodate and scale as needed.
AI has a pivotal role to play when it comes to bolstering sustainability efforts in existing ERP systems. With its powerful computing and predictive capabilities, AI can make substantial strides toward creating more sustainable operations. A standout aspect of the technology’s contribution is enhanced data analysis. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data in real time, providing valuable insights and predictive analysis.
But AI's role continues after data analysis. It extends to creating predictive models that could significantly impact transportation modes and routes. An AI-powered ERP system can analyze numerous variables, including fuel consumption, travel time, weather conditions and traffic patterns. Such granular analysis can be a game-changer in optimizing routes, saving energy and reducing carbon emissions.
Solution and Implementation
By integrating AI capabilities into its operations, the logistics company demonstrated the capability to embrace change. This transformative journey required a series of systematic steps, each crucial in its own right.
Beginning with system configuration, the focus was tailoring the AI-based system to fit the company's unique needs. Here, the AI modules were customized to ensure they could effectively address the specific challenges and objectives of the organization. With a keen eye for detail, every function and feature was tweaked to align with the overarching goal of sustainability.
The next step was data integration. At this stage, the identified ESG data points, which had been painstakingly determined earlier, came into play. Integrating those data points with the AI-powered ERP system allowed for creation of a central data repository that was crucial for real-time analysis and decision-making.
The final piece of the implementation puzzle was employee training. To realize the full potential of the AI-enhanced system, the workforce needed to understand its functionality and potential. A comprehensive training program was developed, ensuring that employees could effectively use the system and interpret its outputs.
The narrative of this logistics company's solution implementation provides valuable insights into the careful planning, execution, and people management that go into integrating advanced technologies like AI. It's a testament to the feasibility of such initiatives and the potential benefits they can bring in promoting sustainable practices.
Sustainable Practices in Action
Having embraced AI-enhanced capabilities, the logistics company began operationalizing various sustainable practices within its transportation operations.
One of the more striking aspects of the transformation was AI-powered route optimization. Sophisticated algorithms analyzed real-time data, identifying the most fuel-efficient routes for logistics operations. This intricate application of AI resulted in substantial reductions in fuel consumption and, consequently, carbon emissions. Additionally, the company incorporated an eco-friendly mode-selection process. AI's predictive capabilities enabled it to determine the most energy-efficient modes of transportation based on factors such as distance, load and environmental conditions.
Lastly, the implemented system allowed for meticulous carbon emission tracking. The company comprehensively understood its environmental impact by quantifying emissions data across the entire supply chain. This insight enabled it to meet regulatory requirements and helped it define more precise and achievable sustainability targets.
Results and Benefits
The real litmus test of any initiative lies in the tangible outcomes and benefits it delivers. In the case of the logistics company, the results have been nothing short of impressive.
A key outcome has been a substantial decrease in carbon emissions across the company's transportation network. Utilizing an advanced route-optimization and navigation platform, a prominent delivery service company has been able to cut down its emissions and optimize delivery paths drastically. By employing sophisticated algorithms, AI and machine learning, the platform has proven exceedingly effective, shaving off approximately 100 million miles yearly since its inception. This has translated into significantly savings of 10 million gallons of fuel, and cut 100,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
The company’s commitment to sustainability has paid off in more intangible ways as well. It has positioned itself as a forward-thinking player in the industry, achieving a competitive advantage. It has attracted environmentally conscious customers and fostered valuable partnerships with other sustainability-focused organizations. And it has shown how a blend of business intelligence, technological innovation and environmental stewardess can set a compelling example for others in the industry.
The story of the logistics company's transformative journey illuminates the broader implications of sustainability in business, mainly when underpinned by advanced technologies like AI. The case study is a testament to how these tools, when integrated thoughtfully, can drive significant strides in the sustainability of business operations. It showcases that environmental stewardship and business prosperity can coexist and complement one another, shattering the conventional belief that the two are naturally at odds.
These outcomes aren’t limited to one particular business or industry. The methodology and results can be replicated across multiple sectors. The hope is that this case study sparks inspiration and encourages other businesses to explore similar technological solutions. It invites others to contribute to a collective vision of a more sustainable future. And it proves that making strides in sustainability isn't just about meeting an environmental obligation, but also about uncovering new avenues of innovation, efficiency and profitability.
Bidyut Sarkar is a senior solution manager of consulting services with IBM. Rudrendu Paul is an AI expert at Boston University.







